How Ketamine Helps the Brain Heal: A Look at Its Long-Term Molecular Effects
June 12, 2015How Ketamine Helps the Brain Heal: A Look at Its Long-Term Molecular Effects
While many people have heard that ketamine can provide rapid relief from depression, fewer understand why it works. Beyond its fast-acting effects, ketamine also helps your brain heal and rewire itself, creating long-term change.
In this post, we’ll break down the sustained molecular effects of ketamine in simple, everyday language—and share one of the most helpful scientific diagrams explaining this process.
Ketamine: More Than a Quick Fix
Ketamine’s benefits aren’t just about feeling better in the moment. It actually triggers changes deep in the brain that last well beyond the day of treatment.

Breaking Down the Science: How Ketamine Heals the Brain
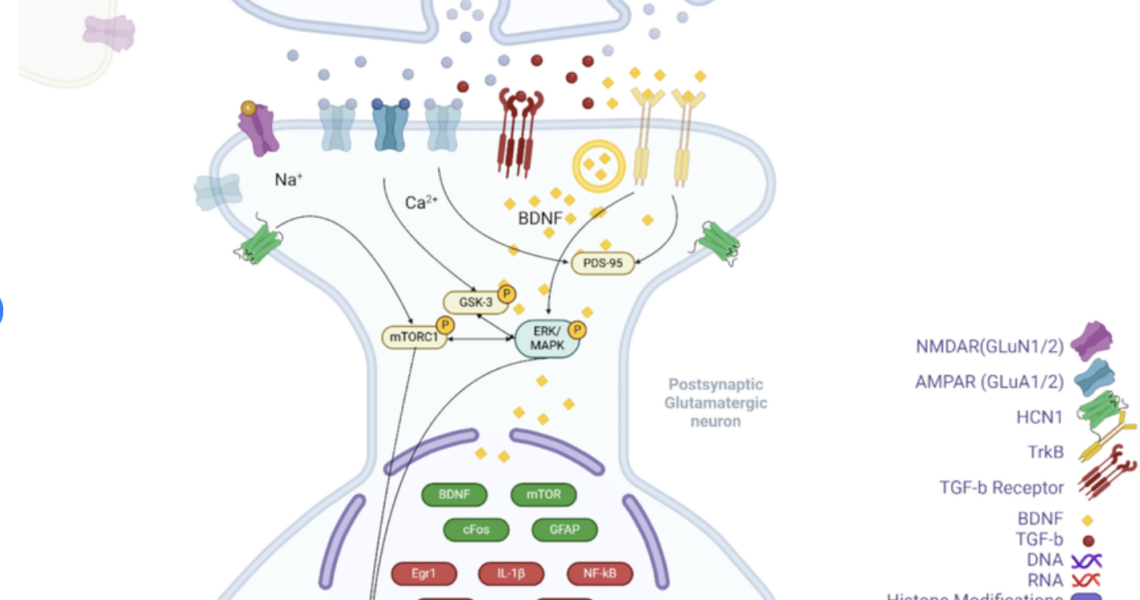
Here’s how ketamine works in the brain, step by step:
1. It helps brain cells communicate better.
Ketamine blocks a receptor called NMDA, which reduces the “overwiring” often seen in chronic stress and depression. This helps calm the brain and reset its signaling patterns.
2. It boosts brain growth.
Ketamine increases a protein called BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor)—often called “brain fertilizer”—which helps grow and repair brain cells and strengthen new connections.
3. It activates healing pathways.
BDNF turns on a series of pathways (like mTOR and ERK) that help the brain build new neural connections. Think of them as construction crews repairing damaged roads in your brain.
4. It supports brain flexibility.
Ketamine inhibits GSK-3, a molecule that normally restricts brain plasticity. By reducing GSK-3 activity, ketamine encourages your brain to become more adaptable and open to change.
5. It turns on helpful genes.
The pathways ketamine activates also switch on genes that are essential for healthy brain function. This is like flipping the switches that control how your brain repairs itself.
6. It rewrites brain “settings.”
Ketamine influences how your DNA is read—changing long-term gene expression by modifying chromatin structure. This helps reset some of the patterns created by long-term stress or trauma.
7. It reduces brain inflammation.
Chronic inflammation in the brain is a major factor in depression. Ketamine lowers inflammation by suppressing pro-inflammatory signals like IL-1β and TNF-α, helping your brain return to a healthier state.
8. It protects your brain.
Ketamine also promotes neuroprotection—helping brain cells survive and function better, even in the face of ongoing stress.
Why This Matters
we see ketamine not just as a treatment, but as a catalyst for healing. By creating the right biological environment, it allows psychotherapy to go deeper—and helps people reconnect with parts of themselves that have been buried under stress, trauma, or depression.
These molecular effects help explain why so many of our patients report profound shifts after just a few sessions of KAP.
Interested in Learning More?
We collaborate with licensed therapists across the country to offer safe, thoughtful, and holistic Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy. If you or someone you love is exploring new options for mental health treatment,we’re here to help.